As we surf the net, we’re all flooded with cookies, plus the annoying pop-ups asking us to accept or deny these digital crumbs. Yet what are cookies exactly, how do they shape our digital experience and are they good or bad? We created this guide as a recipe for anyone who wants to understand these tiny digital files, and what the consequences are if you agree to them (or not!). They may be sugar-free but too many can harm the health of your online privacy. If you’re concerned about who knows what as you search and browse online, consider Avira Secure Browser. It helps block ads, trackers, and browser fingerprinting.
What are cookies and why do they even exist?
If they’re not filled with chocolate chips, why are they even there? We hear you. We’re referring to internet cookies (or to give them their formal name, HTTP cookies)—the tiny files of numbers and letters that are downloaded onto your computer whenever you visit a website. They’re “baked” (created) by the server as soon as you land on a web page and stored in your browser where they act as a unique ID for you and your computer. When you visit that website again, the server reads your cookie ID and knows what information to serve you, such as a personalized greeting, your preferred language, and tailored ads or product recommendations. Cookies also store information for marketing purposes, including how users engage with a website, and how long they stay. Advertisers and companies use these digital traces to build profiles on website visitors, so cookies aren’t just there to enhance your online convenience and enjoyment. For many people that’s reason enough to regularly delete cookies from the browsers on all their devices—whether it’s a laptop or PC, Windows or macOS device, as well as Android or iOS smartphone or tablets.
The next time you’re greeted cheerfully by your name online, in your language, or see an ad for sports clothes after you’ve googled “gyms near me”, you can be sure it’s not a coincidence: Cookies have been hard at work!
What are the different types of cookies? Should you accept them?
As soon as you visit a website for the first time, there it is—that pop-up consent notification we all know so well: “We use cookies…”. You’ll typically be prompted to make one of three choices:
- Either you accept all cookies,
- You reject them, or
- You customize your consent.
And, if you’re like most users, you’ll simply click “accept all” so you can proceed. Who has time to mess around with tiny text files when there’s online shopping to be done, for example? Before you next wield your mouse at a cookie pop-up, take a moment to consider the upsides and downsides of your response based on the type of cookie you’re dealing with. Broadly speaking, you’ll encounter four kinds based on what they’re used for:
- Essential (or strictly necessary) cookies help ensure that the website displays and functions correctly. They’re used exclusively by the website operator and allow you to interact with the site, such as log into secure areas and use the shopping cart.
Accept or decline? Don’t worry about it. Companies don’t require your consent for this type of cookie, and you can’t reject them.
Privacy rating: High. This type of cookie shouldn’t collect any personally identifiable information and is not designed to track browsing habits.
- Functional cookies help enhance a website’s performance, functionality and personalization. They allow video playback and social media sharing, for example, and remember a user’s language and region—but keep this stored information anonymous.
Accept or decline? These cookies require your consent to work but shutting them off means some parts of the website may not function as intended.
Privacy rating: High. These cookies are anonymous and shouldn’t track browsing activity across other websites.
- Performance cookies analyze user behavior, such as the length of their visit, the sequence of sub-pages viewed, and even the search terms they used to find the website. With the help of this information, website operators can identify popular content, bounce rates, and improve site performance.
Accept or decline? These cookies require your consent to work, but you can rest assured that the data they collect is meant to be anonymous. In the long run, these cookies can help developers improve the usability of a website and companies can provide content relevant to potential customers. Will you help them? It’s up to you.
Privacy rating: Acceptable. If these cookies are doing their job correctly, the data can’t be traced back to you and your browsing habits aren’t being tracked.
- Marketing cookies are often set by advertisers—also known as third-party providers—so they can display personalized ads tailored to your interests. You can generally activate and deactivate them in your browser’s cookie settings. (More on how to tinker with your settings later).
Accept or decline? These cookies require your consent to work, so you have a choice. Bear in mind that they track your online behavior, including clicks, shopping choices and even device specifications and search history. How much do you want to give away?
Privacy rating: Low. These tracking cookies help advertisers and marketers build detailed profiles on users to serve targeted ads. They can also collect personally identifiable information such as your name, email address, phone number and other information you enter on website forms. To help protect your privacy, regularly clear your browsing search history.
First and third-party cookies: What’s the difference?
Broadly speaking, the cookies mentioned above fall into two additional categories depending on who set them and who they are available to: We’re talking about first-party and third-party cookies, and it’s the latter that often worry people.
First-party cookies are created by the website you’re using. If it’s a reputable site and hasn’t been compromised by a recent data breach or cyberattack, these cookies are generally considered safe.
Third-party cookies are generated by websites other than the one you’re currently surfing on, usually because they’re linked to ads displayed on that page. They allow advertisers and analytics companies to track your browsing history—so they’re like a trail of digital breadcrumbs across all the sites that contain that company’s ads. You won’t know where your data will end up though and what it could be used for. Most websites will work fine and remember your preferences even without third-party cookies. Many browsers are now working to eliminate or restrict them to help limit how we’re tracked across the web and to give us greater control over how our online data is used. Google plans to phase out cookies for all its Chrome users by Q3 2024 and has already switched off cookies for around 30 million users!
How long do cookies last and should you clear them?
Cookies are also described based on their duration. Session cookies are short-lived and expire when you close the browser or your web session ends. E.g.: When you fill out an online form. As the name suggests, persistent cookies can hang about for weeks, months or even years. They remain on a device until they reach their expiration date, or the user clears them from the browser.
Clearing your cache and cookies regularly is considered good “tech hygiene,” and can help you troubleshoot, such as if your device is feeling sluggish or web pages are loading slowly. Avira System Speedup helps declutter your machine of all the stuff that may be slowing you down, like temp files and duplicates. In addition to more space, you could also experience faster starts and smoother performance. (Get it alone or as part of Avira Free Security).
Accept or banish? How should you respond to cookies?
As you’ll have learned by now, cookies can work to your advantage. They can speed up your browsing experience and logins, websites may work better, and you’re more likely to see content that’s relevant to your personal preferences and interests. There are times when it’s recommended NOT to accept or keep them though:
Beware the third-party cookie: If you don’t decline these, the website could sell your browsing data and other personal details to third parties.
If your computer is slowing down. They may be tiny, but cookies take up disk space and storing legions of them repeatedly can clutter up your machine.
You’re on an unencrypted website: If there isn’t a locked icon beside the website address, the web page isn’t securely encrypted and hackers could steal your cookies, helping them gain access to your online accounts. This is called cookie hijacking, or session hijacking, and is a dangerous type of man-in-the-middle attack. Secure websites are called HTTPS sites.
Avira Secure Browser helps block websites that use the less secure HTTP encryption and helps keep you safer from phishing websites and infected downloads. As an anti-tracking browser, it also helps cover your digital footprint.
How to clear cookies in your browser on your desktop PC or Mac
In addition to allowing you to block third-party cookies, all browsers give you the option to clear cookies once you close the browser. Beware of the latter. You’ll be logged out of any websites and your saved settings may also be deleted. If you want to manually remove or manage cookies from within your browser, click on your browser icon below. And see here to start clearing cookies on your mobile device.
Deleting cookies in Internet Explorer
Microsoft recommends switching to Edge because Internet Explorer is no longer being updated. Nevertheless, here’s how to delete cookies in this browser:
- Click the Tools icon (looks like a wheel) on the right of the address bar and click Internet options.
- In the window that opens on the left, click Delete to open another window that offers various options for deleting your browsing history.
- Various data categories are already preselected here, including Cookies and website data.
- Click Delete to confirm your selection. Once done, you’ll have deleted your cookies.

Clear your browser cookies in Google Chrome
Google guides you in detail through the various options for deleting, allowing, or managing cookies in Chrome—whether you want to automatically block all third-party cookies, clear cookies when you close all windows, or customize which websites are allowed to store cookies and which are not. Follow these steps to start managing cookies in Chrome:
- On the top right, click the kebab icon (the one with the three vertical dots) followed by Settings.
- Click Privacy and security, and then select Clear browsing data.
- Choose from Basic or Advanced options and tick the relevant boxes. The basic tab gives you the option to clear your Browsing history, Cookies and other site data, and also Cached images and files. The Advanced tab lets you also choose Passwords and Auto-fill form data.
- To confirm, click Clear data.

Clearing cookies in Mozilla Firefox
There are various options around deleting cookies for your current or any website, site data and the cache in Firefox.
- Click the hamburger icon (the one with three lines) in the top right corner. Then select Settings.
- Choose Privacy & Security on the left and scroll down to find various settings under Cookies and Site Data.
- Click the Manage Data button. The Manage Cookies and Site Data dialog will then appear.
- You can choose to sort the list of websites them by storage volume.
- Now select the websites with cookies you want to delete and click Remove Selected (or Remove All), followed by Save Changes.
- You’ll then be prompted to confirm that you want to remove the cookies for the selected website(s).

Removing cookies in Safari
Apple Support carefully guides you through various ways of accepting or blocking website data and cookies in Safari on a Mac. Here’s a quick run-through:
- In the Safari app on your Mac, choose the Safari icon at the top left, select Settings, and then Privacy.
- If you click Prevent cross-site tracking, you can prevent tracker cookies from being used. These cookies and website data will be deleted if you avoid those websites that use tracking cookies.
- If you select Block all cookies, websites, third-party providers, and advertising companies will generally not be able to store cookies or other data on your Mac or Windows PC or laptop. However, this setting may prevent websites from working correctly.
- Click Manage Website Data, and you’ll be able to select individual or multiple websites and delete the associated cookies by clicking Remove or Remove All.

For a comprehensive digital cleanup, it’s a good idea to regularly clear out the system cache on your Mac.
Clearing cookies in Opera
- Go to the address bar and click the Opera icon on the left. Then scroll down and select Settings followed by Privacy & security. Now click Clear browsing data.
- Tick the box next to Cookies and other site data.
- Select the Basic or Advanced tab. Choose the time range you want to clear cookies for, or to clear all your cookies, choose All time. The Advanced tab will offer the same selection, as well as options, such as to clear passwords and autofill form data.
- To end off, click Clear data.

Deleting cookies from Microsoft Edge
You can delete all cookies or just cookies from a specific website in Microsoft Edge, and set Edge to automatically delete cookies every time you close your Edge browser.
- Go to the address bar and click the three horizontal dots on the top right. In the dropdown menu, scroll down to Settings.
- In the window that opens, click Cookies and site permissions.
- Now choose Manage and delete cookies and site data.
- Select See all cookies and site data and a list of all the websites that have stored cookies in your browser will appear.
- You can now either hit Remove all or decide page by page which cookies to delete.

Deleted your cookies? Now help optimize your device and your online protection
Whether you’re looking to digitally declutter or improve your privacy, clearing cookies is a great first step. It’s worthwhile to consider a tune-up tool to keep things running more smoothly. Avira Free Security comes with a built-in optimizer that helps free up space and can contribute to faster starts. It also adds a free VPN and Password Manager if you’re serious about online privacy, while its Free Antivirus helps keep you safer from even zero-day threats.
Don’t forget your mobile! Delete cookies on your iPhone, iPad, Android, and laptop
It’s easy to forget that cookies also accumulate on our smartphone or tablet via a browser app. Check for and remove these cookies regularly.
Android user?
Here’s how to delete cookies from the Samsung Internet browser app.
- Open the Samsung Internet browser and tap Settings.
- Under the Advanced section, tap Sites and downloads and then Manage website data. A list of all the websites that have used cookies and stored them on your smartphone will appear.
- You can either remove these individually (or all at once) by selecting the websites and clicking Delete.

iOS fan?
Here’s how to delete cookies from the Safari app on your iPad or iPhone.
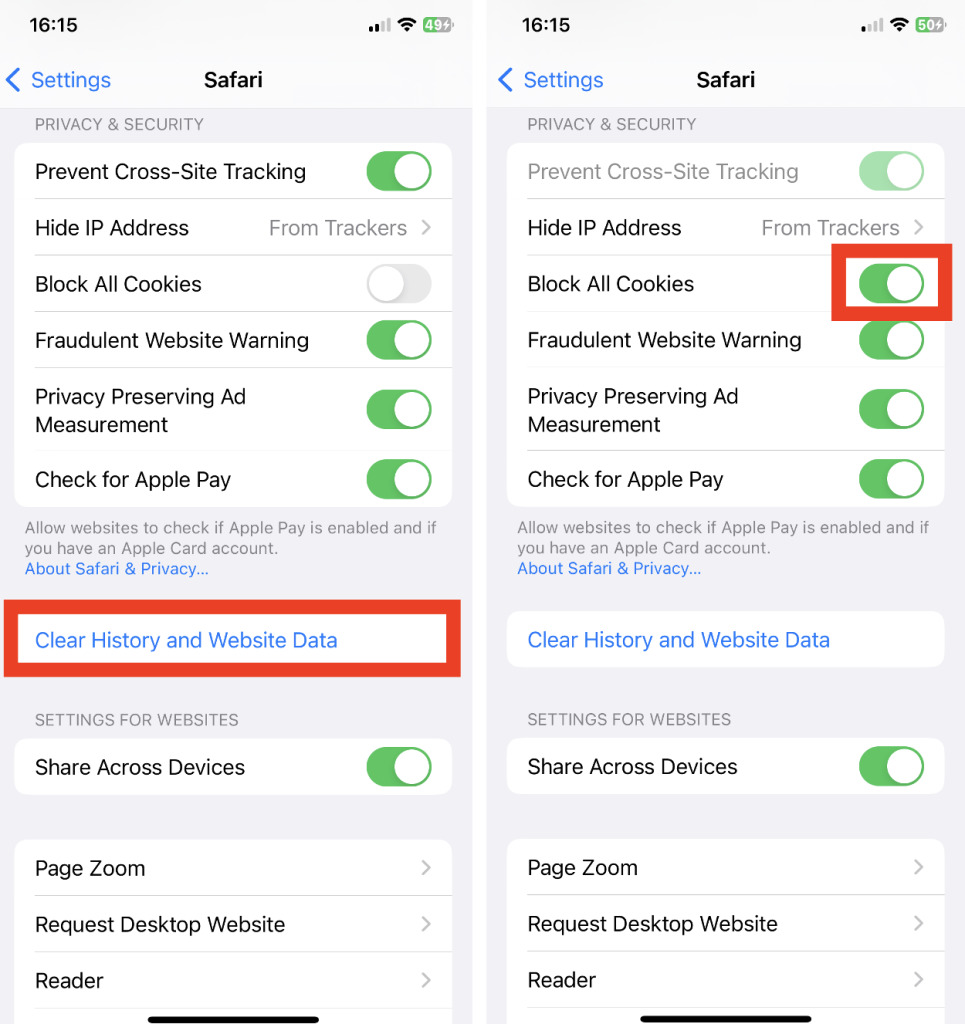
Safari offers extensive options to delete and manage cookies on your iPhone, iPad, or iPod Touch. You can choose to clear your cookies but keep your history, for example. Follow these steps to get started quickly:
- Open the Settings app.
- Swipe up to find Safari.
- Tap Clear History and Website Data. Note: Clearing history, cookies, and search data from Safari won’t change autofill information.
If you want to remove only the cookies but keep your history, open the Settings app and tap Safari. Then scroll down to select Advanced. Click on Website Data, and then tap Remove All Website Data. For a zippier device, remember that it’s always a good idea to carry out a regular iPhone cleanout.
To continue optimizing your iOS device and online privacy, consider a multi-pronged solution like Avira Free Mobile Security for iOS.
Chrome user? Here’s how to clear cookies on your iOS or Android device
- Open the Chrome app on your smartphone or tablet.
- Tap the kebab icon (the one with the three vertical dots) on the bottom right, followed by Settings.
- Tap Privacy, and then Clear Browsing Data.
- Select your desired time range.
- Tap to tick Cookies, Site Data, and Cached Images and Files, and remove the tick from all other options.
- Now tap Clear Browsing Data followed by Clear Browsing Data once again.
Avira Secure Browser focus
Browsing, posting, shopping…whatever we do online, digital traces are inevitable, and you’ll load up on enough cookies to rival a bakery. While these tiny files aren’t always inherently bad, they do contain personal data and can clutter up your computer over time. If you want to keep your actions online more private and stop companies building profiles on you, consider a privacy-focused browser like Avira Secure Browser. Its Web Shield is designed to help block fake and dangerous websites and downloads so you’re more likely to thwart phishing attempts as well as trackers.





















